The evolution of automotive safety features
Automotive safety has undergone a remarkable transformation since the inception of the motor vehicle. Initially, the focus was rudimentary, centered on basic structural integrity. Over decades, a continuous drive for innovation, fueled by research into accident causation and occupant protection, has led to increasingly sophisticated systems. This evolution reflects not just technological advancements but also a deeper understanding of human factors in driving and the dynamic environment of roads and transport.
Early Automotive Safety and Design
In the nascent years of the automotive industry, safety considerations were relatively basic. Early vehicles often lacked fundamental features that are standard today. The primary focus of vehicle design was on mechanical reliability and performance, with passenger protection largely secondary. Seatbelts, for instance, were not widely adopted until much later, and crumple zones were conceptualized only after extensive research into crash dynamics. Materials used in early manufacturing were often rigid, transferring significant impact forces directly to occupants, highlighting the need for innovation in structural integrity and occupant containment.
Advancements in Passive Safety Technology
The mid-20th century marked a significant shift towards integrating passive safety features designed to protect occupants during a collision. This era saw the widespread introduction of three-point seatbelts, which dramatically reduced fatalities and severe injuries. Concurrently, engineers began to incorporate crumple zones into vehicle designs, strategically deforming upon impact to absorb kinetic energy away from the passenger compartment. Airbags emerged as a supplementary restraint system, deploying rapidly in a crash to cushion occupants. These developments, alongside reinforced vehicle structures and improved interior materials, collectively enhanced occupant protection, making travel safer for everyone on the roads.
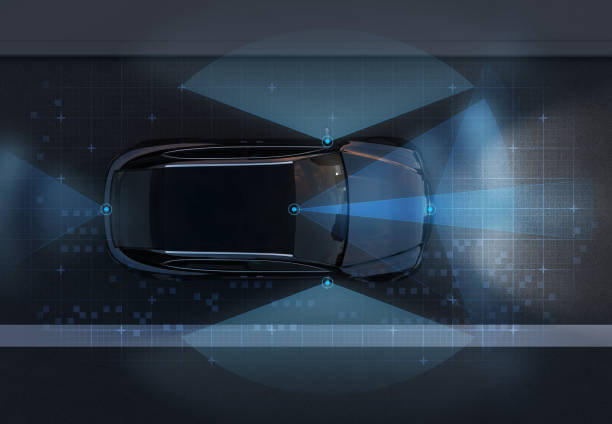
The Rise of Active Safety Systems and Driving Assistance
The turn of the 21st century ushered in the era of active safety systems, which aim to prevent accidents from happening in the first place. This paradigm shift was largely driven by advancements in automotive technology, including sensors, cameras, and sophisticated electronic control units. Features such as Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS), Electronic Stability Control (ESC), and Traction Control Systems (TCS) became commonplace, helping drivers maintain control of the vehicle under challenging conditions. These innovations in driving assistance represent a proactive approach to safety, leveraging technology to mitigate risks before a collision occurs, thereby improving overall mobility and reducing incidents on busy transport networks.
Future Directions: Autonomous Vehicles and Sustainability in Safety
The ongoing evolution of automotive safety is increasingly focused on autonomous driving capabilities and sustainable practices. Autonomous vehicle technology promises to significantly reduce human error, which is a major contributor to road accidents. Features like adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assist, and automatic emergency braking are precursors to fully self-driving cars, representing advanced steps in vehicle intelligence. Furthermore, the development of electric and hybrid vehicles introduces new considerations for safety, including battery protection and pedestrian warning systems. The automotive industry is also exploring lighter, stronger materials and more sustainable manufacturing processes that do not compromise safety performance, ensuring that future mobility solutions are not only safer but also environmentally responsible and efficient in their engine and component design.
Integrating Digital Technology for Enhanced Protection
The integration of digital technology continues to redefine automotive safety. Beyond autonomous driving, connectivity features are playing an increasingly crucial role. Telematics systems, for example, can automatically alert emergency services in the event of a severe crash, providing precise location data that can significantly reduce response times. Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication systems are also under development, designed to allow vehicles to share information about road conditions, traffic, and potential hazards, further enhancing predictive safety measures. This constant innovation in technology and design is geared towards creating a more interconnected and inherently safer driving environment, transforming the entire experience of travel and vehicle interaction on modern roads.
The journey of automotive safety features reflects a continuous commitment to protecting drivers, passengers, and pedestrians. From rudimentary designs to sophisticated electronic systems and the promise of autonomous vehicles, the trajectory is clear: a relentless pursuit of greater security on the roads. This ongoing innovation, driven by technological advancements and a deeper understanding of accident prevention, continues to shape the future of transportation and mobility. The focus remains on leveraging cutting-edge solutions to minimize risks and enhance the well-being of all road users.






